What are the different types of profit?
When looking at business accounts there are 4 key types of profit:
- Gross Profit
- Net Profit
- Profit Before Tax
- Profit After Tax
In this blog I’m going to show you what each type of profit is and how to work them out for your own business accounts.
How to work out the different types of profit
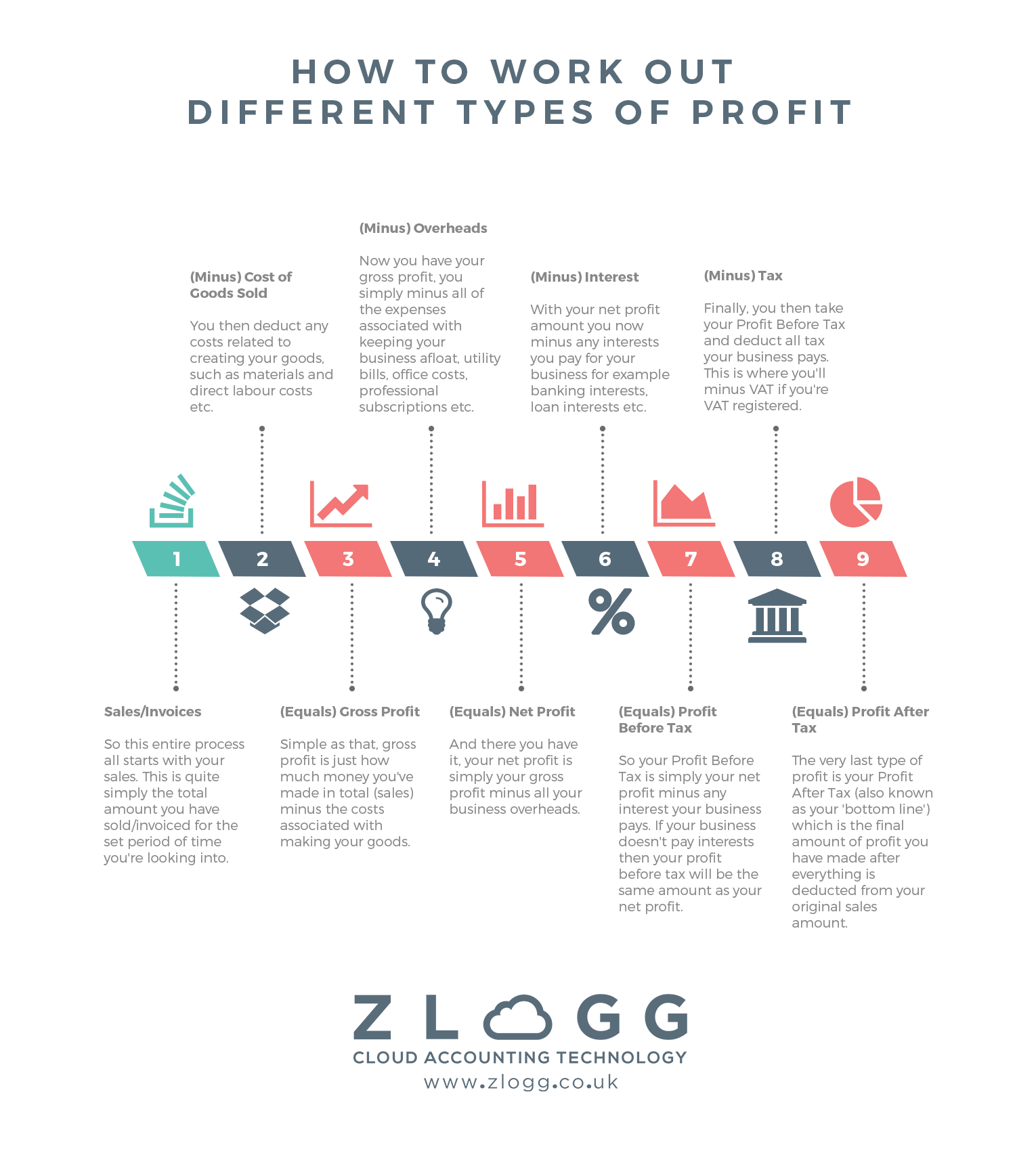
When it comes to each of the 4 key profit types I find the easiest way to remember them all is in the form of a ‘timeline’ because each one follows on from the next as shown in the infographic below which makes it a simple 9-step process:
As you’ll see all profit types flow perfectly from one to the next making it very easy to remember how you calculate each one. Feel free to download our profit types infographic and keep a copy so you always have it to hand whenever you need reminding!
So now you’ve seen the diagram let’s explain how this timeline of profit works:
1. Sales
So this entire process all starts with your sales. This is quite simply the total amount you have sold/invoiced for the set period of time you’re looking into. This is excluding VAT if you are VAT registered.
2. (Minus) Cost of Goods Sold
You then deduct any costs related to creating your goods, such as materials and direct labour costs etc.
3. (Equals) Gross Profit
Simple as that, gross profit is just how much money you’ve made in total (sales) minus the costs associated with making your goods.
4. (Minus) Overheads
Now you have your gross profit, you simply minus all of the expenses associated with keeping your business afloat, utility bills, office costs, professional subscriptions etc.
5. (Equals) Net Profit
And there you have it, your net profit is simply your gross profit minus all your business overheads.
6. (Minus) Interest
With your net profit amount you now minus any interests you pay for your business for example banking interests, loan interests etc.
7. (Equals) Profit Before Tax
So your Profit Before Tax is simply your net profit minus any interest your business pays. If your business doesn’t pay interests then your profit before tax will be the same amount as your net profit.
8. (Minus) Tax
Finally, you then take your Profit Before Tax and deduct all tax your business pays. This is where you’ll minus VAT if you’re VAT registered and is why you must list all sales in step 1 without VAT.
9. (Equals) Profit After Tax
The very last type of profit is your Profit After Tax (also known as your ‘bottom line’) which is the final amount of profit you have made after everything is deducted from your original sales amount.
Why are there so many different types of profit?
I completely understand this seems like an endless list of profit types, however the reason for there being so many different types of profit is because each version allows you to see your business profits from different angles and assess where your business is making or losing the most money.
For example, your gross profit may be really good, but then you suddenly realise that when you deduct your overheads to get your net profit…you no longer have a profitable business! This would raise alarm bells and make you realise you need to drastically deduct the amount of overhead costs your business is paying out for in order to have a truly profitable business.
There are plenty more examples of course, but the simple fact is that each type of profit allows you to see your how much your business is making by deducting different variables step-by-step.













Share On